
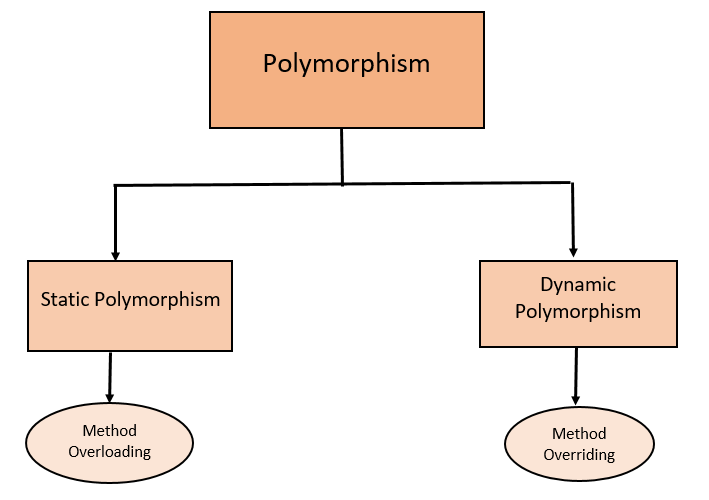
Both have their uses in object-oriented programming and it is not that one outweighs the other. If the binding is changeable at runtime, as in the case of polymorphic references where the decision of binding is made only during execution, it is called dynamic binding or late binding. When a reference variable is bound to an object that cannot be changed at runtime, or, in other words, the binding of method invocation to a method definition is done at compile time, it is called static binding. This leverages flexibility by giving another dimension of use of the reference variable.

Therefore, if a reference can be used to invoke a method at one point in time, it can be dynamically changed to point to another object and invoke some other methods the next time.
The rule is too rigid, but polymorphism makes is more flexible by incorporating the idea of “having many forms.” This means that a polymorphic reference guarantees that it can refer to different types of objects at different points in time rather than being stuck with the idea of an exact match for compatibility. This may seem to be the only reliable condition, but that is not exactly true, especially when implementing polymorphism. The qualification of the reference variable to a referred object is determined by its compatibility. The ‘ employee‘ is a reference variable that may refer to an instance of the Employee class. For example, in the following case: Employee employee It is typically compatible with the class that it refers to. Polymorphic Reference: An OverviewĪ polymorphic reference is a variable that can refer to different types of objects at different points in time. This article explores some of the intricate details about polymorphism and its implication on object-oriented programming. Although creating polymorphic reference in Java is easy, the concept behind it has a deeper impact on overall programming. In object-oriented methodology, polymorphism enables writing programs that have late binding references. The term typically means that something that can have multiple forms. Polymorphism is one of the fundamental principles of Object-Oriented Software. We may make money when you click on links to our partners. content and product recommendations are editorially independent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
